

Please observe:
The following listing is preliminary and not complete.
Our goal is to introduce a design procedure for building a high-quality modular audio mixing console. Modular refers to a design that can be split into smaller portions (modules) so when complete, they can be joined together to form one system. A modular audio mixer is formed by assembling some main modules that can be varied in number and/or disposition to suit individual needs. Being determined to motivate electronic engineering students to be involved on analog circuits design from not just a theoretical and mathematical perspective, we have implemented an educational platform in order to encourage learning in practice.
Due to the demographic evolution there is an increasingly pressing question for additional support in the healthcare. Technology can relieve this pressure by providing tools for automated monitoring and objective assessment of a person’s health condition towards a long-term and ambulant follow-up.
In this research project, which was part of a PhD, three practical cases were treated. The first case described how demented elderly in the final stage of their life can be observed to determine their discomfort level. In the second case adults were asked to wear a simple knee sensor and physical activities were determined automatically. In the third case, paediatric patients suffering from epilepsy were monitored during the night and abnormal activities were indicated.
This resulted in three different monitoring setups but they all have in common that they consist of sensors which can easily be placed in the room of the patient and/or attached to the patient. Monitoring systems were designed to be as comfortable as possible for the monitored person/patient in order to make long-term observation feasible. Also off-the-shelf technology was used to reduce cost and time-to-market. And finally, all these systems were implemented and validated in practice in order to contribute to a faster integration of technology in the healthcare sector.
Mechatronics is concerned with the development of as well intelligent production lines as intelligent products. In our current society they take an ever more increasing role as these systems can be found anywhere. Ranging from home environments such as digital cameras, to industrial environments such smart agriculture machines.
The software part of these Cyber Physical Systems is becoming more important as more and more components are programmable. This talk will focus on software engineering strategies that support the development of embedded software for CPS’s. Focusing on current research in agile methodologies such as test driven development and techniques to build resilient embedded software. This resilience copes with disturbances in software leading to dataflow or control flow errors. This resilience is positioned in relation to functional safety standards to which these systems must adhere.
The analysis of feet by clinical experts (podiatrists, orthopedic technicians, orthopedic surgeons) is mainly based on the knowledge they built up over the years. Also the techniques and equipment that are used can vary from expert to expert according to their personal preferences.
To aid the expert in the foot analysis, different measuring equipment is available. In our study, we investigated the following ones: a 3D marker based motion registration system, a force plate, a plantar pressure plate, a dynamic 3D scanner and high speed cameras.
In this first study, we investigated the link between the clinical analyses of the experts and the quantitative measurements of the hardware systems. In a next step we want to know where the hardware can improve the analysis.
Different features are extracted from the quantitative measurements. The experts’ scores are predicted by training an SVM classifier with the features as input and the experts’ scores as output. We used different sets of input features, mimicking the fact that we use different subsets of hardware. The SVM’s are tested in a leave-one-out cross-validation. To estimate the robustness, this cross-validation is repeated 10 times on a randomized subset of the full data.
We found that no unique measuring system is perfect for the prediction of all foot characteristics. Sometimes specific hardware is good for the prediction of a characteristic, often a combination of systems is better. For example, the calcaneus in relaxed position and the midfoot pressure are best predicted by a combination of a pressure plate and a marker based motion registration system. If we look at only one system, the motion registration system gives satisfying results for the former characteristic whereas the pressure plate gives best results for the later case.
With contemporary developments pushing towards an ever connected world, spearheaded by the push for the ’Internet of Things’ coupled to all things ’cloud’, security still remains an afterthought. Cost is often cited as the main reason, followed by the ever shorter deadlines and competition to bring devices to market as fast as possible.
In this paper we will review some of the recent issues with a wide variety of connected devices and show how lacking security decisions ended up costing the end users as well as the implementers. Additionally, we present a possible solution to one of the core issues: trust in the communications network, or the lack thereof. In addition, we will report a project with a currently deployed, networked device which adheres to accepted security requirements while still being cost effective.
Olive fruit production is of crucial importance in the Mediterranean basin (only Greece has an annual revenue of more than 1.6 billion euros from the olive oil industry). One of the main threats for the aforementioned type of cultivation is the Bactrocera oleae (Gmelin) or Dacus oleae (Gmelin) (Diptera: Tephritidae) mostly known as fruit fly, which damages annually more than 30% of the olive oil production in the Mediterranean countries. The most common method for protecting the olive trees is by monitoring the population of the flies to decide and perform bait sprays so that to eliminate the threat. These processes is time consuming, requires a lot of manpower for monitoring the population and perform the spray baits, and it is often inefficient due to the fact that the appropriate decisions are not taken on time.
To overcome the aforementioned problems we have developed a 3 layer novel system based on embedded system devices which: (i) allows to monitor remotely and in real time the bug population, (ii) process the available information in a web server and take optimal decisions on time and (iii) perform the bait spraying in an optimal manner and simultaneously record the process for data meta processing. This system provides a framework able to (a) assure proper application of bait sprays by minimizing human intervention, (b) improving the health and safety at work and (c) offer a more effective and efficient protection of the olive fruit production againt B. oleae with simultaneous improvement of the produced olive-oil in terms of both quantity and quality.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work is implemented within the context of the Operational Program "Education and Lifelong Learning" action Archimedes III, Project 25, and is co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund) and Greek national funds (National Strategic Reference Framework 2007 - 2013).
Modern batteries and their production tolerances make it necessary to equalize the state of charge between single cells in order to maximize the capacity and the longevity of the battery pack.
To balance these cells there are two usual methods. One of them is passive balancing which restores the balance between cells by discharging the higher charged cells and wasting this energy as heat. The other method is active balancing which reaches the balancing goal by transferring energy from the cells with a higher state of charge to the lower ones. In both techniques energy already charged in a battery cell is wasted and additional to this the aging of the battery cells is accelerated by extra charge and discharging cycles in the balancing process.
To bypass those negative effects another balancing method could be used. Using this method the state of charge of the single cells could be balanced while charging. Therefore no energy shall be transferred between cells but a special charging electronic will make it possible to charge single cells additional to the main charging process of the battery pack. The cells with a lower state of charge would get extra energy to equalize the battery pack.
This technique could be used to increase the longevity of expensive batteries especially in energy storages systems since battery and charger form a connected unit.
RFID-based access control systems and contactless payment cards are used by various applications in people’s everyday lives. Nevertheless only a few know how this technology actually works. The information security of the access control systems has not been discussed in public even though several different hacking methods for the systems have been developed and published. Implementation of contactless payment cards has received a lot of attention, but with regard to security, media attention has still remained rather low.
The main security problem is that, in general, technology used today is too old and the new systems are made to be compatible with them; which is continuing poor security technology. The second problem is that because the technology follows open standards, hacking methods are available to the public. Also, security risks are increased by mobile phones with NFC-interfaces using free hacking applications. However, the technology is still quite secure because the problems are generally not well known.
This article presents: the basics of RFID technology, information security methods and several different hacking methods that have been published in one form or another. Information security of contactless payment cards will also be covered and the current security situation will be assessed. The unsecure state of RFID-based access control systems and contactless payment cards are studied and presented.
Several years ago navigation systems were mostly integrated into high class cars, their use was mainly limited to people which were able to pay tremendous prices for these systems. These days the situation has changed completely: Car Navigation systems are available for reasonable prices that many people can afford, and navigation systems are now integrated into almost every smartphone. Therefore many people do have the possibility not only to navigate from their current location to a defined destination but also to make use of their current location within various smart phone apps.
However, today’s market regarding navigation systems, may it be in cars, smartphones or other devices, is dominated by systems using access to the US-based GPS [1]. Nevertheless, a selection of states within the European Union supported by some other countries is currently developing and deploying a new European Navigation System: GALILEO [1] [2]. The intention of this presentation is describe the European GALILEO System and to provide insight into the planned applications of GALILEO as well as the current status [3] [4] [5]and trends within the development of GALILEO.
REFERENCES
[1] J.-M. Zogg, GPS und GNSS: Grundlagen der Ortung und Navigation mit Satelliten, Schweiz, 2014.
[2] W. Mansfeld, Satellitenortung und Navigation: Grundlagen, Wirkungsweise und Anwendung globaler Satellitennavigationssysteme, Vieweg-Teubner Verlag,
2009.
[3] Spiegel-Online, „Navigationssystem Galileo: Europäische Satelliten in falscher Umlaufbahn ausgesetzt,“ 23 August 2014. [Online].
Available: http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/weltall/navigationssystem-galileo-satelliten-in-falscher-umlaufbahn-a-987668.html. [Zugriff am 7 September 2015].
[4] Spiegel-Online, „Navigationssystem Galileo: Perfekt verpeilt im Orbit,“ 28 Oktober 2014. [Online].
Available: http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/weltall/navigationssystem-galileo-panne-koennte-navigation-verbessern-a-999475.html. [Zugriff am 7 September 2015].
[5] Spiegel-Online, „Navigationssystem Galileo: Zweiter Satellit erreicht korrigierte Umlaufbahn,“ 19 März 2015. [Online].
Available: http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/weltall/galileosatelliten-erreichen-korrigierte-umlaufbahn-a-1024402.html. [Zugriff am 7 September 2015].
Source Code Management (SCM) systems are software solutions that provide coordination, collaboration and communication within a software development team. File management and version control components are the key elements of such systems, giving developers the ability to work concurrently on the same files, merge changes and trace previous changes. In the proposed solution-based module for SCM systems, the main objective is the determination of the programming language that has been used in a source code file.
One of the most popular methodologies to solve this problem, is the use of file extension, which unfortunately is not an efficient-reliable way to determinate the category of a source code file. Usage of metadata presents the big problem that it does not suffice to effectively classify programming source code files because none can guarantee that file extension clearly represents the content of the file.
Different approaches are trying to provide an efficient method for source code management, using a combination of computational Intelligence techniques. However, the stability and the adaptivity of each system are usually contradict each other. The proposed solution-based approach is trying to minimize erroneous results by increasing the overall system’s adaptivity using Artificial Neural Networks with a simple textual filtering derived from fuzzy set theory. The implementation of the artificial neural network was based on a multi-layered perceptron topology with back-propagation learning rule. Moreover, using a set of fuzzy logic algorithms, an amount of free parameters were excluded leading to a significant reduction of the required data for the calibration process of the overall system.
Computational Intelligence techniques are able to provide excellent results using concepts defined at different levels of abstraction, in order to effectively solve conceptual problems like Natural Language (NL) problems or a more restricted form of NL problems such as source code classification – programming language detection. In applications such as SCM systems a kind of the proposed mechanism could provide adaptation and reliability.
In case of an emergency an ambulance team needs to reach the destination swiftly and safely and in many cases needs to return to the hospital with a patient at a matching pace. The ambulance crew needs two kinds of skills: driving skills and emergency treatment skills. Driving skills can be improved through training in closed track. The missing factor in the track training is the traffic – it is not feasible to have dozens of cars to simulate the traffic conditions that an ambulance driver will on an average emergency call. Emergency treatment skills are part of paramedic training but putting them in practice in a moving ambulance is quite different from training in the class. Both of the mentioned issues can be addressed in simulator training.
A simulation platform was developed for this purpose. The platform can be used both for driver and emergency treatment training. The training system consists of a motion platform that is used to simulate the movement of the ambulance and ambulance driving simulation software that controls the motion platform. The simulator enables driver and paramedic training in a safe environment with realistic feel of the ambulance movement.
Industry 4.0 is based on the following concepts: Internet of Things, the Internet of Services, and Cyber-Physical Systems.
In order to implement Industry 4.0 scenarios, we have to look at the following underlying design principles:
Vaasa University of Applied Sciences (VUAS) is constantly faced with new challenges because it is responsible of providing the Ostrobothnia region with young graduates who are capable to actively participate in the economic growth of more than 100 companies in the ICT sector that represent the core of Vaasa welfare. The key challenges are the adaptation of the curriculum to the needs of the industry, the fast changes in the needs and the wide spectrum of technologies used by different business. These are real constraints and any change requires a lot of time to be really efficient. Unfortunately we don’t have enough time to cope with these challenges. The other constraints other than time are the traditions and history of the organisation that make the process to accept new curriculum a mission impossible. Therefore, a desire to overcome these constraints is to create different channels for students to effectively gain the most from the available resources of VUAS and use these resources to provide added value for the local industry. To achieve this goal, it was necessary to create an educational entity that is entirely free from any constraint that may cause delays in decision making. Such entity was called the Industrial Innovation Academy (I2A). Industrial Innovation Academy (I2A) is a structure that acts as a bridge between education and industry, to challenge students with real problems. The goal of I2A is to create an environment where students could develop better professional skills and work on real projects provided by the industry as well as develop own innovative ideas for the industry. The I2A with the feedback from the industry evaluate the students work and can provide the student with equivalent ECTS. A personnel study plan (PSP) is usually made as a contract for students who choose to take part of their studies at the I2A.
I2A includes several workshops which focus on projects related to Software Engineering, Energy ICT Systems, Embedded Systems, Robotics and Telecommunications. The I2A projects portfolio is being constantly expanded. I2A is a part of Vaasa University of Applied Sciences and all its workshops are located in Technobothnia Research Center.
In this presentation the speaker will describe the organisation of the I2A, give the details about its operation and demonstrates some real projects that have been done for the local industry.
This article considers lessons learned and sharing of best practices within the development of concurrent courses and modules in embedded systems education and implementing them in the partners universities in Ukraine, Georgia and Armenia, in the course of a European Tempus project.
The article considers an example of the advertisement network based on the BLE 4.0, and its facilities for creating the infrastructure for a Smart Campus, where dynamic information is provided for the target audience. The authors provide an analysis of the characteristics and experimental implementation of this system. Moreover, the practical usage of a popular vendor and the needed back-end to provide dynamic usages of the network, both in appearance and content is described. In the paper different wireless technologies are compared in regards to their main feature and field of application. In general the characteristics of a Blue Tooth Low Energy, BLE, are highlighted. This is elaborated upon in the Smart Campus example. The Smart Campus is an indoor wireless network to deliver location and user based dynamic information to the different visitors, teacher or students of a university campus, both for day-to-day use as for specific events. To keep the system interesting and to augment ease-of-use for all kind of users and content providers, a dedicated content management system is developed within the Smart Campus case. The complete system consists of a set of beacons, an application on a smartphone, a database with the related CMS. All is developed in an international cooperation between different universities.
Objectives
Due to the ageing population, more elderly people will depend on the support of others. Automatic monitoring systems that can detect and report deviations from regular behavioral patterns can aid in giving this support. Several sensor types can be used in such a system. This exploratory study focuses on sensors that can measure the electrical current of appliances linked to activities of daily living (ADL) (e.g., cooking, cleaning, etc.). Knowing if and when a person uses electrical appliances can give valuable insight in ADL patterns. This abstract describes the provisional results of the first step towards automatic recognition of ADL: classification of electrical appliances with machine learning algorithms.
Method
A dataset was constructed using 11 electrical appliance types (TV sets, coffee machine, vacuum cleaner, etc.) as listed in Table 2. Each appliance was measured with a current sensor several times for two seconds during its normal working regime with a sample frequency of 5kHz, resulting in 109 instances. From this data, seven features were extracted: Irms, Imax, correlation of the electrical current with a perfect sinewave, crest factor, harmonics, power and standard deviation of fluctuations in envelope. The data set is split up randomly into a training set of 85 and a test set of 24 instances. As exploratory experiment, we compared three classification algorithms on accuracy: Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes and Nearest Neighbors (kNN, k=1..3). The platform we used was the Raspberry PI 2, a low cost Linux computer. The classification is done with Mathematica from Wolfram Alpha, which comes installed for free in the Raspbian (Linux) operating system image.
Results
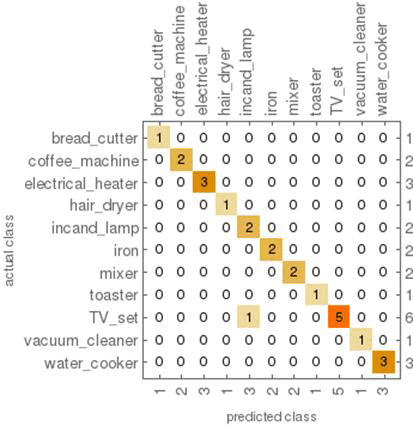
The comparison of the accuracy of the three algorithms is shown in Table 1. All three algorithms obtain good performance results and the best result is obtained with the kNN-approach with k = 1. This indicates a near perfect prediction can be done if we first measure the relevant appliances in the house and use those as a training set for detection. The confusion matrix for classification using kNN with k=1 on the test set is shown in Table 2.
Algorithm |
Accuracy |
Logistic Regression |
75% |
Naïve Bayes |
79% |
kNN, k = 1 |
95.8% |
kNN, k=2 |
87.5% |
kNN, k=3 |
87.5% |
Table 1: Accuracy measure
Discussion and future work
With this experiment, we showed that it is feasible to recognize electrical appliances from their electrical current signature on a low cost platform such as the Raspberry PI 2, running the Mathematica software. In the future, we will further investigate into the generalization
of the recognition of appliances and into developing a real time monitor system based on the Raspberry PI. Real time sampling and classification will contribute significantly in developing an automatic monitoring system for those ADL that rely on the usage of electrical appliances.
In today’s world organizations can no longer afford to underestimate or ignore the threat attackers pose. Organizations have learned to reduce threats through a combination of technological, administrative and physical measures designed to address a specific range of problems.
On the other hand, effective hacking is a process that takes place in phases. Each phase of hacking is undertaken with the goal of uncovering increasingly useful information about a target that can be used in the eventual break-in. The steps of the information-gathering process include:
We introduce the project DIANA, which deals with the development of innovative algorithms and decision support systems for the design of public transport network systems with application to the city of Heraklion - Crete. The project aims to design transportation networks, with the objectives of maximizing total welfare, considering multiple contradicting criteria. A particle swarm optimization algorithm is being developed for solving the associated transit route network design problem.
Public transportation is a sustainable option for transportation in urban areas, offering advantages such as mobility enhancement, traffic congestion and air pollution reduction, and energy conservation while still preserving social equity considerations. The design of such a public transportation network is a complex optimization problem, which involves a variety of design parameters (route structure, frequencies, vehicle types, etc) and assumptions on demand patterns, travel behavior and so on. Indeed, the associated Transit Route Network Design Problem (TRNDP) has been a topic of interest for over 40 years.
Following prediction of flows, our model attempts to design a bus network operated by two vehicle types (conventional and electric) by taking into account operator, user and external (environmental) costs. Three design variables are considered: route structures, frequencies and vehicle types. Major assumptions are the following: (i) vehicles for each type are of the same, constant capacity, (ii) demand patterns are assumed fixed according to the solution of the problem, as extracted previously (iii) demand follows a “many-to-many” pattern, as the network is expected to connect multiple origins and destinations and (iv) a limited number of transfers between routes is acceptable, while direct connections are preferred.
A generic representation of the proposed model is the following:
Minimize (Passenger cost + Operator cost + External cost) = f(demand satisfaction, average travel time, pollutants emitted, charging stations required, vehicle types)
under the constraints of
Resource availability (available vehicles per type)
Operating constraints (minimum and maximum frequencies, capacity constraints, possible charging stations)
Binary particle swarm optimization (B-PSO) is used for solving the model. Therefore we use a binary representation for the solution vector. For L lines and S bus stops gives a vector with LxS bits. The each bit is set to 1 if the respective line includes the associated bus stop. Additional bits encode the bus frequency and the use of electric or conventional vehicles for each line.
The objective function aims at minimizing the weighted sum of user, operator and external costs; it consists of six components: unsatisfied demand and average travel time (proxies of user cost), pollutant mass (external costs), charging stations, conventional vehicles and electric vehicles required (proxies for operator cost). Unsatisfied demand refers to the demand that cannot be satisfied neither directly nor through a single transfer. The average travel time per passenger includes both in-vehicle travel time and waiting time, while emissions refer to air pollutants emitted exclusively by conventional vehicles.
We define a set of constraints in the following way:
- A charging station is required in at least one terminal stop of a route for electrical vehicles.
- A set of nodes with adequate space for the deployment of charging stations.
- We set route length limits upper bounds for preventing delays and for minimizing the risk of energy depletion in case of delayed arrivals to charging stations.
- We set the minimum and maximum route frequency values
- We set resource availability constraints, referring to the maximum number of conventional and electric vehicles.
- We control the structure and directness of a route by preventing the omission of neighboring bus stops, as well as route backtracks and U-turns.
The approach has been applied for the city of Heraklion - Crete. We used 50-80 nodes to represent the bus stops and 10-15 different bus routes. A solution gives a route combination, which is sub optimal. The visualization is supported via integration with Google maps.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The DIANA project is implemented through the Operational Program "Education and Lifelong Learning" action Archimedes III and is co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund) and Greek national funds (National Strategic Reference Framework 2007 - 2013).
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) is expected to be one of the technologies that will revolutionize the world by 2022i. MOOCs are online courses, usually free, that are open for anyone in the world to take. MOOCs became famous when in the fall of 2011, Sebastian Thrun of Stanford University launched an online, open access course on Artificial Intelligence.160,000 students from 190 countries were enrolled but only 23,000 successfully completed the course.
This research implemented, that is funded by the Erasmus KA2 project called Destiny, through face to face and online interviews that took place in three different Universities in three different countries, aimed to identify: (a) the impact of the MOOCs in the Higher Education in Europe, (b) the missing skills that the Labour Market (LM) need for employment and (c) how MOOCs can be used to address the missing technical and soft skills that our graduates lack in order to satisfy the market needsii and thus fight the high unemployment among youths in Europe.
Preliminary results regarding the skills missing in LM and the teachers’ and students’ recognition of MOOCs will be presented. The survey was conducted among undergraduate & postgraduate students and teaching staff of engineering, natural science, finance and business Departments in four different countries. The online and personal interview responses were analyzed using SWOT analysis’s tools. The whole research was implemented on the frame of the Erasmus Plus DESTINY project funded by EU.
Finally a short research on the availability of MOOCs in the Ambient Intelligence and Embedded system has been performed. The revealed results demonstrate an intensive effort in the development of MOOCs in the artificial intelligence, neural networks and embedded systems. The most interesting result was that one of the existed MOOCs in embedded systems is one of the top 10 most popular MOOCs.
iK. Pretz, “10 technologies that could change the world by 2022”, IEEE – The Institute, 12 November 2014
iihttp://www.mckinsey.com/features/education_to_employment
The EmSys Embedded Systems group from Thomas More University College, specialized in the design, development and production of embedded systems will be presented.
EmSys focuses on different target markets like e.g. health and vitality, work and mobility, sciences and exploration, automation and industry and not in the least education.
During the presentation the development of a mobile an wearable orthese socket pressure sensing system and a implantable knee angle, proof of concept, measurement
system based upon commercial of the shelf components or C.O.T.S. will be explained.
The presentations ends with possible (inter)national Bachelor/Master thesis subjects
proposals at the EmSys research group on Campus de Nayer.
Integrated CMOS circuits are essential in today’s high-energy physics experiments like the CMS ant ATLAS detectors at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in CERN. Since ionizing radiation, created by these high energy particles, degenerate the silicon performance and circuit signal integrity, radiation hardened electronics are necessary. In this field of research, various circuit techniques are investigated to cope for the problems created by ionizing radiation. Typically, long term silicon degeneration (mobility and threshold voltage) and single-event-effect transients are taken into account. Calibration methods and high speed recovery circuits are used in this field to reduce the effects of ionizing radiation. Such circuits are designed at both circuit and architectural level and need to be transparent to the high level system.
The major tasks of Battery Management Systems (BMS) are to guaranty safe operation conditions and to maintain every single cell of the whole battery pack. These tasks require measurements and balancing processes for each cell. Especially new lithium ion cell chemistries reveal hard conditions on the BMS to estimate hardly measurable state variables like the State of Charge (SoC) or the State of Health (SoH). The capability to exactly estimate these conditions represents the fundamental requirement for economical operation of the battery pack. Different procedures for SOC estimation are applicable. The standard coulomb counting method or the referencing of the Open-Circuit-Voltage (OCV) and model based observers like the Kalman-Filter are promising candidates But these methods also have a central weakness. Depending of the used cell chemistry the dependency of the OCV of the SoC is small and furthermore the OCV is difficult to measure precisely enough to estimate precisely the SoC. Therefore a novel estimation method needs to be developed to properly determine the actual SoC.
This lecture describes a method to estimate the SoC for every single cell based on impedance spectroscopy measurements. For that purpose a genetic algorithm (GA) is developed running on an electronic control unit (ECU) of the BMS to determine five significant parameters representing o model equation which offers the opportunity to estimate the actual SoC. The impedance for each cell from 50mHz to 5Hz at ten frequency steps is measured. This range characterizes the SoC dependence significantly. These data are analyzed by the develop GA running on the BMS master and the estimated parameters describe the corresponding charge. Besides the SoC further more information can be extracted from the impedance and allows drawing conclusions about the SoH of each cell
Olive fruit production is of crucial importance in the Mediterranean basin (only Greece has an annual revenue of more than 1.6 billion euros from the olive oil industry). One of the main threats for the aforementioned type of cultivation is the Bactrocera oleae (Gmelin) or Dacus oleae (Gmelin) (Diptera: Tephritidae) mostly known as fruit fly, which damages annually more than 30% of the olive oil production in the Mediterranean countries. Monitoring the population of the flies is of crucial importance since based on that, decisions are made so that actions can be taken to protect the olive trees. The monitoring is the last decades, is performed using McPhail traps, which are filled with a chemical substance that attracts the bugs. These traps are deployed in vast areas of interest usually with thousands of trees and specialized personnel are monitoring the population of the flies inside the traps in a weekly basis. This procedure is problematic since there is no assurance of taking the decisions on time but only upon the weekly counting of the bugs. Another main issue is that a lot of manpower is essential. To address this problem we have designed, developed and tested a novel trap which is equipped with an embedded device able to record the population of the flies and transmit the information using the GSM network to a remote server where the agricultural scientists are using this information to take proper actions on time. In the context of this paper we will describe in detail the components of the novel system and we will present preliminary results.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work is implemented within the context of the Operational Program "Education and Lifelong Learning" action Archimedes III, Project 25, and is co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund) and Greek national funds (National Strategic Reference Framework 2007 - 2013).
This article highlights new teaching approaches and course development in the field of embedded systems, within an international European Tempus project with a consortium of higher educational institutes from the EU and partners in Ukraine, Georgia and Armenia. It considers lessons learned and sharing of best practices within the development of concurrent courses and modules and implementing them in the partner universities. Considerably effort is attributed to strengthen the ties with industry in the field of embedded systems.
The paper elaborates on the scope of the project, preliminary analysis of competences needed for the local and international labor market, the intended goals of the project and strategies used in quality, dissemination and management of the project. In detail it deals with the courses developed, thematically divided in courses for hardware, software, CAD/CAM/CAE and some additional courses, all with learning disabilities in mind, ways to train the teachers on the new material and ways to support students with the newly delivered equipment. All is done in a blended learning way, with the use of distance learning, hands-on, remote and virtual laboratories. Finally this article deals with the risks and challenges of international projects of this scope and intermediary results.
Different resource meters are part of almost all human invented devices and gadgets. Typical known examples are battery level indicators of mobile devices or gasoline level indicators of cars. In more complex systems there might be tens or hundreds of indicators telling status of different critical resources, remaining expected lifetime of critical components or just readiness of service (heartbeat) at the instant. Logging of set of important parameters is often used for off-line analysis the service quality of the systems, in some of cases such post-analysis is extremely important to discover exact reason of catastrophic failure like in case of “black boxes” of planes and other large vehicles. Still, as it is known the observable history of black boxes is limited, covering only limited number of last service hours.
Contemporary systems have started to obtain certain level of (self-) awareness, meaning ability to assess development of internal and external “world” according to certain fixed of flexible self-trainable model. Such systems are able to predict own ability and quality to fulfil defined goals in near future on base of past service history and current situation.
The paper is analysing possible indicator designs to represent history of service over system full lifetime, averaging far past events to limit information stored to non-volatile memory. To reach that different classification scenarios are used to discriminate regular events and anomalous (critical) ones which are requiring special attention because might negatively impact probability to fulfil defined goals in future. The running pattern of system past “life” could be a part of self-awareness property of the system itself, i.e. additional feedback to increase precision of prediction the service quality in near future.
This presentation presents a possible way of writing a Linux device driver for an embedded platform. The
presentation shows the example of the mainline accepted PWM device driver for the raspberry pi, written by the
author and accepted November 2014 in the mainline Linux kernel.
First of all, the presentation handles the PWM subsystem of the Linux kernel. This is the standard interface for
using a PWM hardware block in the Linux kernel. All the necessary characteristics of the PWM output can be
changed within this framework.
Second, the presentation tackles the PWM hardware at the raspberry pi platform. The driver will translate the
PWM subsystem structure of the kernel to the PWM hardware available on the platform.
As last, the presentation shows some scripts and tools to check the driver before committing it to the Linux mailing
lists and hopefully, get accepted and pulled into the Linux kernel.
Linux become more and more the basic operating system (also the basis of android) for embedded systems.
But embedded systems are more flexible and exists in much more flavors than the standard x86 desktop computers.
First of all, the output pins of embedded systems can be used by different hardware blocks and has to be set by the
pin multiplexer.
Second, the available hardware blocks are very dynamically on different chips. For example, the processor and bus
architecture of a Beagleboard is identically to a Zedboard but the available hardware blocks are different.
To tackle this problem, Linux has introduced devicetree (http://devicetree.org/Main_Page) support.
The presentation shows the possibilities of device tree support in Linux by showing demo's on development boards
like Raspberry Pi, Udoo and Zedboard.
Scratch (https://scratch.mit.edu/) is a programming environment developed by MIT and used to learn
young students (starts at the age of 8) to program. This free tool has a very good graphical interface and learns the
students to think as a programmer.
This presentation handles the use of scratch in combination with a raspberry pi embedded platform (running
scratch on the raspberry pi or at a x86 host) and shows how to extend the functionality of the scratch environment
by sending network packets to the board and run a night rider demo.
We present an innovative methodology that combines hardware and software techniques for flexibility, through essentially employing low-cost on-line monitoring, debugging and real-time replacement of the failing sections of software algorithms in an embedded multi-core system.
This project focuses on the implementation case-study of ciphers into multicores embedded systems. The outcome between four ciphers into a system of three cores, which is based on a prototype platform of Xilinx, Virtex-6 CXT FPGAs, is also tested. Moreover is attempted to evaluate the reliability of the encryption and decryption of a processed image comparing with the results from the corresponding algorithm of a processed image from MATLAB. The Complicated ciphers are widespread in the microelectronics. This is design of a system two processors where implemented in a selected image processing (supports various image sizes) with the application of the algorithm edge detection Sobel. The second processor is implemented encryption application, the already processed image, the algorithms TEA, Present, Blowfish and AES.
The results of the processed image verified by the respective exporting the MATLAB for the same image. Third processor running Online Monitoring algorithm. The application starts by placing the image we want to work in the local memory of the processor is responsible for processing the image. Then the Sobel algorithm detects image edges and outputs the processed image, shown in pixel values 255 or 0. Both processors are connected with Fast Simplex Link provided by Xilinx and the end of the algorithm Sobel, informed the second core to start the encryption and decryption of the processed image. The processed pixel (data) we have arranged to be stored in the external memory of the FPGA DDR to access the second processor, which encrypts and decrypts data. The proposed mechanisms introduce negligible performance degradation, reduced hardware cost and require minimum code instrumentation.
The techniques towards reliability presented in this work are not overly intrusive in the design process and are largely transparent to the embedded applications. Our contributions pertaining to this context are two-fold. We focus on enhancing reliability in the execution of coprocessor tasks with a priori known execution times by allowing an embedded system to identify anomalous software behaviors and additionally to provide rapid online reconfiguration and re-execution in run-time. We present an innovative methodology that combines hardware and software techniques for flexibility, through essentially employing low-cost on-line monitoring, debugging and real-time replacement of the failing sections of software algorithms in an embedded multi-core system. The proposed mechanisms introduce no performance degradation, reduced hardware cost and require minimum code instrumentation.